Illustration by Sean Nyffeler of Popcorn Noises fame
PREVIOUSLY, in Part 1: Some background on recommendations and expectations, and UHD defined. [Click here to view the entire piece as a single page.]
UHD isn’t as esoteric as it seems
I realize that, at first, UHD just seems like a wonky way to describe something that’s already obvious and intuitive. But it actually has real-world applications, especially when it comes to understanding our intuitive-but-not-easily-explained preferences for stuff.
For example, UHD helps me understand why it took me a little while to move from CDs to downloading MP3s 1. Initially, the cost of an MP3 album (on iTunes, for example) was pretty close to the CD and Apple was using DRM 2. My concern was that I wouldn’t “own” the music if I paid for the MP3s. The result was that the utility of the MP3s was less than that of the CD, even though it was the same music at the same cost. Since the cost was similar, and the hours of entertainment would be the same, the difference in utility made the UHD for CDs higher than MP3s. Eventually, Amazon started offering DRM-free downloads and cheaper prices, shifting the UHD for MP3 downloads ahead of CDs. That’s when I made the switch to MP3 downloads 3. Of course, I didn’t actually do a conscious UHD calculation one day and say, “Ah ha! The UHD for MP3s is finally greater than it is for CDs! Time to make the switch!” But that’s basically what happened. The same process is happening for me with eBooks right now. 4
A brief, anecdotal history of cinema
The shift from CDs to MP3s, or from physical books to eBooks is interesting to me. But what’s really interesting to me is the persistence of movie theaters despite cheaper, very similar movie-watching options. Fifty years ago, the only real option for seeing a movie was to go to the movie theatre. This was great for movie companies because they could charge high prices since they were basically the only game in town. The UHD calculation wasn’t really useful for deciding how to watch a movie because it wasn’t so much a matter of comparing different movie-viewing options as just deciding whether it was worth it to spend the money on a movie or not. If it wasn’t, you just had to find something else to do.
Then technology started changing, opening the door for the home theatre experience. First, VHS started enabling people to watch movies at home en masse. Hi-fi began morphing into fancier surround sound setups whose cost was dropping so that more and more people could buy them. LaserDisc 5 came and went. Then DVD took hold and made the home-viewing experience even better.
A sidebar into UHD for movies at the turn of the century
Ten years ago, we really had two options for watching a movie (without owning it). We could either go to the theatre or rent it at Blockbuster. Let’s run through the UHD calculations real quick, just to get an idea of the difference in UHD for these two options at that time:
- A good movie as a “New Release” rental was about $4 (-ish), lasted 2 hours and provided a utility of 6:
- 6 utils * 2 hours = 12 util-hours
- 12 util-hours / $4 = 3 UHD
- The same good movie in the theatre would have been about $5, lasted 2 hours and provided a utility of about 7 (slightly higher since it was in the theatre):
- 7 utils * 2 hours = 14 util-hours
- 14 util-hours / $5 = 2.8 UHD
So the UHD for renting versus going to the theatre was really close even as recently as 2000. They were close enough that there was a real decision to be made: Spend $5 and go to the theatre or spend $4 and stay home? We would often decide what to do based on the number of people in a group (if there were four of us, we could just split the rental for a buck a piece; if there were two of us, then why not just pay for the movie in the theatre?) and our willingness to sneak snacks into the theatre. 6
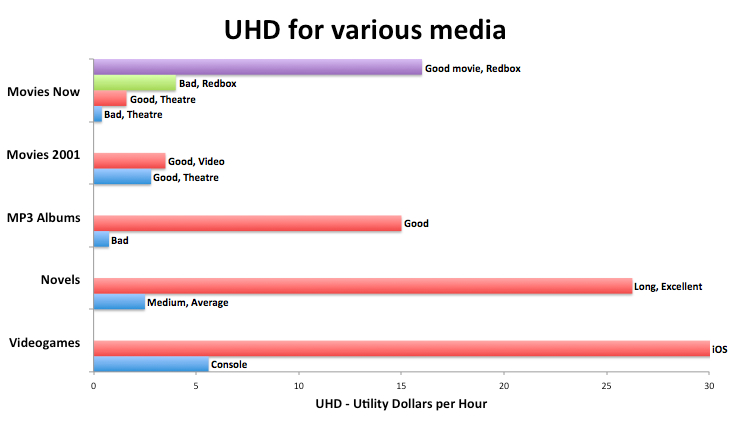
Our trusty UHD chart from Part 1
Snap back to reality
A lot has happened over the past 10 years or so. Netflix popped up, HD-DVD lost the war to Blu-Ray, streaming video became better and better, Blockbuster got crushed, and DVD rentals have gotten cheaper and cheaper. There are options now, options that just weren’t available when movie theaters first became a big deal. Not only are there options, but there are cheap options that rival the actual movie-going experience. And yet, movie ticket prices have been steadily increasing over time. 7
Let’s look at one more sample UHD calculation:
- A really bad movie that I waited to watch on Redbox DVD would be $1, last 2 hours and provide a utility of 2 8:
- 2 utils * 2 hours = 4 util-hours
- 4 util-hours / $1 = 4 UHD
As we saw earlier (in Part 1), watching the bad movie in the theatre gives .4 (that’s point-four) UHD. Watching the same bad movie on DVD gives 4 UHD. Watching the bad movie on DVD is 10 times “better” than watching it in the theatre, and all of this difference is accounted for by the difference in cost. “But wait!”, you say, “What if I enjoy watching movies more in the theatre?! I really like going to the theatre!” Ok, fine. How much better would the movie have to be in the theatre to make up for the difference in UHD?
Some people will want to go to the most extreme case first, so let’s just go straight there. Let’s say that the bad movie moves from 4 utils to 10 utils just because I enjoy going to the theatre so much. It only jumps to 2 UHD (still half of the 4 UHD if I wait to watch the bad movie on Redbox DVD). “That doesn’t make any sense!” My counter would be, “So you’re saying there’s no way any movie can be better than the bad movie in the theatre? What if you go see a good movie in the theater?” Since the 1-10 scale is a subjective scale, I have to leave room above the bad movie for less-bad movies. Either that or I have to slide my Redbox DVD experience down to a 1 or something. If I move the theatre experience up to a 10 and move the Redbox DVD experience down to a 1, then I get the same result for both options: 2 UHD.
The present, seemingly uncrossable gulf between UHD for going to the movies and watching them at home is due to super high, sticky movie prices and much, much cheaper alternatives for watching movies at home. This has created such a big gap in cost that watching movies in the theatre is just that much more expensive, ruining their UHD relative to the very-similar experience of watching movies at home now.
Going to see movies in the theatre is expensive. I realize some people will say, “But your formula is just wrong. It weights the cost too much.” Using the UHD calculation as-is, it’s hard to see many situations where it would be better to go to the theatre than to watch the flick at home. It’s possible that I’m weighting cost too heavily, but I think the real problem is that movie theaters are just way too expensive now because we have more, better options. There really is that much of a difference in cost between movie theaters and rentals.
Movie Expectations – A bizarre special case?
And yet, new releases continue to set box office records as people go to the theatre in droves. At the same time, the movie theaters are much more expensive than the alternatives, and the quality of the movies released has been consistent (or at least not improving enough to justify the growing gap between theatre prices and the alternatives). What gives? If I’m right that waiting for the movie on DVD is almost always better than going to the theatre, then why do so many people continue going to see movies in the theatre? Why did I go see three movies in the theatre this summer?
I’ve overheard this sentiment several times recently: “That movie wasn’t that bad. I just went into it with no expectations and it turned out ok. I’ve decided I just won’t have expectations for movies because I end up over-hyping them and when they don’t meet my expectations I feel ripped off.” So the idea is that movies are often bad because we expect them to be good, or at least because we expect them to be better than they actually are. To solve this problem, we play mind games with ourselves, intentionally under-hyping a movie so that when we go see it and it’s just an ok movie, it exceeds our deflated expectations.
At first, I saw the wisdom in this tactic. If we get really good at lowering our expectations, almost any movie will be a success, at least inasmuch as it will exceed our expectations. That way, we can pretty much guarantee that when we pony up $10 for a ticket and another $10 for concessions, we won’t be let down.
The more I think about this, the more ridiculous the idea seems. We don’t lower our expectations for music, books or TV shows, do we? So why do we do that with movies? Of all our options, movies are one of the most expensive. Why would we trick ourselves into doing something super expensive that we don’t really enjoy that much?
UP NEXT, in Part 3: Why we game the UHD system, what it costs us, and how much all this matters. [Click here to view the entire piece as a single page.]
- Ok, ok. It took me a while to purchase MP3s, but we’ve all been downloading MP3s since the Napster days (or earlier via AOL chatrooms and such, right?). The fact that I can still download all the free music I want, and that I don’t do that is a tangent I just don’t feel like taking right now. That said, I do think it’s pretty interesting that I (and a lot of other people) pay for music now when I used to (and still can) just get it all for free.
- DRM is basically a way for content providers to help protect their copyrighted work by dictating how many (and what kind of) devices the purchased stuff can be played on. It’s basically dead (or almost dead) for music, but is alive and well for video.
- The last CD I bought was Cool Kids’ “Bake Sale“.
- I’d say it’s more or less inevitable that we’ll all eventually be streaming MP3s (or maybe I should drop the “MP3” label and just say “music”) with some sort of subscription (think Spotify) instead of purchasing via download. The problem is almost the same as my problem with switching from CDs to MP3s, only switching from “buying” an MP3 to “streaming services” (essentially leasing access to a catalogue) is a bigger paradigm shift that people are very, very slowly embracing. This shift has already happened with streaming video. I can’t really think of any reason to buy a DVD anymore. It just seems like a waste when I can probably stream it online whenever I want. The irony is that we’re making the buy-to-stream shift faster with video than with music. I’m still working out why these two seem to be happening out of order.
- LOL.
- When I was a kid, my dad rented movies almost every weekend, but if we went to the theatre, we were absolutely sneaking in some Twizzlers and sodas {a}.
{a} Probably Winn-Dixie brand stuff like Strawberry Check {i}.
{i} I really wanted to include like a Wikipedia link or something with that Strawberry Check reference, but I couldn’t find anything on Google. Am I making that up?
- Movie ticket price increases have more or less tracked with inflation since the 60s {a}. Before that, they increased really quickly, which makes sense since it was a new technology where demand was increasing quickly and the supply (movie theaters) was growing slowly. Eventually, there would be enough movie theaters that anyone who wants to go see a movie can go see it. Then, barring any substantial changes in technology, the prices should flatten out. Eventually, prices would be expected to decrease if there were competitors (direct or indirect) that reduce demand. This is happening now with the proliferation of the home theatre, DVDs, Redbox, Netflix, etc. It makes sense that movie prices should plateau pretty soon because of all the competitors to “movie theatre movies” now.
If you want more data, you can go here to see US Inflation numbers and use a calculator. You can see average ticket prices over time here. Because of really high inflation in the 70s, movie ticket prices actually lag by a few years, but they catch up to inflation in the 80s. There seems to be a larger-than-inflation increase in ticket prices in the 90s, but that doesn’t have a huge effect on the general trend that movie ticket prices track with inflation from the 60s forward.
{a} At least that’s what my few hours of analysis tell me. As far as I can tell, there’s about a 95% correlation {i} between inflation and movie prices since the 60s. It’s entirely possible I screwed this up.
{i} I used the two sources above and the Excel “CORREL” function to get this number.
- I’m using the same utility for theatre and Redbox, basically assuming there’s no difference between theatre and home theatre for most movies now – this isn’t IMAX. Also, this makes the next discussion a little easier.

Webmentions
[…] was originally a three-part series: Part 1; Part 2; Part […]
[…] PrevNext → February 14, 2012Josh DoodyEconomics, Essays, Movies, Music, Reading, Recreation, Technology, […]